Engineered Removals (CDR) activities remove carbon dioxide (CO2) from the atmosphere and durably store it in geological, terrestrial, or ocean reservoirs, or in products.
Three core principles define engineered CDR:
- Captured CO2 must come from the atmosphere, not from fossil fuel sources.
- The storage of captured CO2 must be durable, such that the CO2 is not reintroduced into the atmosphere.
- The removal must be the result of human intervention, additional to the Earth’s natural processes.
THE NEED FOR REMOVALS
Achieving global net-zero requires durable CO2 removal. While reducing emissions must always come first, and mitigation measures have their place, it is widely recognised that to achieve net-zero, businesses must compensate for residual emissions with CO2 that is durably removed from the atmosphere. CDR is therefore not just an option; it is a necessity.
Reaching net-zero without removals is unlikely in the short to medium term, particularly for sectors like aviation and agriculture where sustainable and cost-effective reduction solutions do not yet exist at scale. Natural CDR solutions such as afforestation and soil carbon sequestration play a vital role, but a diverse portfolio of removal approaches, including engineered solutions, offers a more robust and resilient path to achieving global climate goals.
PROJECT TYPES
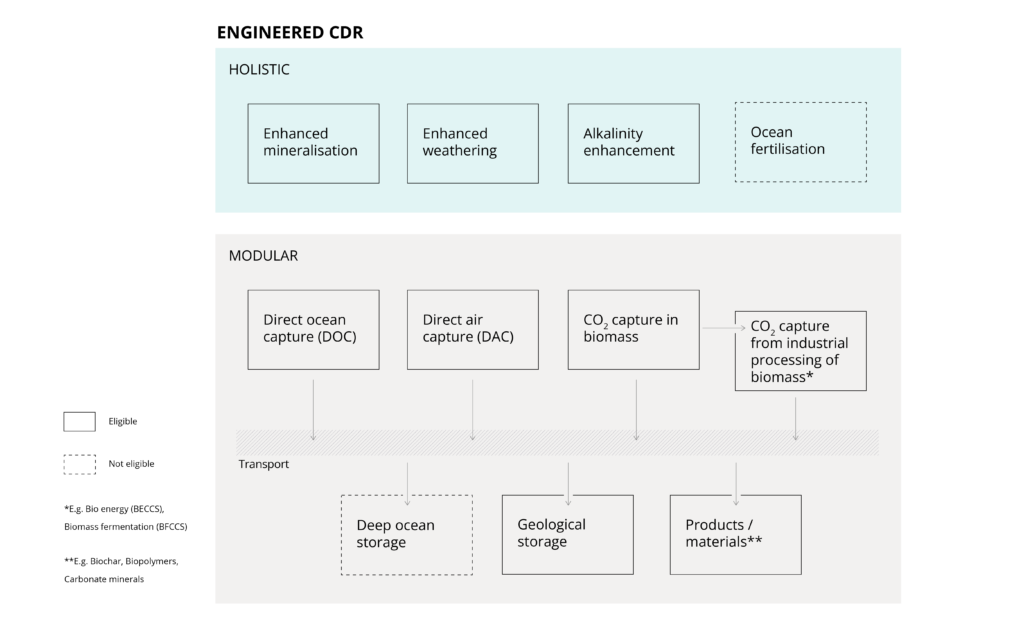
Gold Standard supports the development of both holistic and modular CDR activities.
Holistic engineered CDR solutions integrate capture and storage in open environments, such as enhanced weathering in fields or ocean alkalinity enhancement along coastlines. In contrast, modular engineered solutions separate capture and storage, often involving transport between sites and operating in closed systems, like direct air capture paired with geological storage.
Gold Standard takes a considered approach to engineered CDR activities, focussing only on scientifically robust mechanisms that can deliver a high level of durability certainty and environmental integrity.
VERIFIED IMPACT
Engineered CDR methods, such as direct air capture, carbon mineralisation, enhanced weathering, and biomass processing with carbon capture, utilise technological or enhanced natural processes to capture CO2 and achieve durable storage, typically in geological reservoirs, or long-lived products like biochar.
All Gold Standard engineered CDR projects adhere to robust, science-based methodologies that ensure accurate monitoring, reporting and verification (MRV) of climate impact. By integrating robust MRV, strong ecological and social safeguards and alignment with the United Nations Sustainable Development Goals, our approach delivers verified outcomes with tangible benefits for climate, nature and people.
THE GOLD STANDARD DIFFERENCE
Building on over 20 years of experience in setting the highest benchmark for quality and integrity in the voluntary carbon market, Gold Standard is working to expand its CDR options to help scale this vital sector in a way that positively impacts the planet, people and nature. Gold Standard-certified CDR projects must:
- Follow safeguarding principles to ensure that there are no risks to ecosystems or communities;
- Deliver and quantify wider sustainable development impact, contributing towards at least 3 of the United Nation’s Sustainable Development Goals;
- Establish formal channels to enable inclusive stakeholder engagement throughout the project’s lifetime.
These are Core Principles embedded within the Gold Standard framework and are underpinned by leading technical governance and a robust assurance process, aligned with ISEAL’s Codes of Good Practice.
GS4GG Documents